Introduction
Subsurface exploration has long posed significant challenges across various industries, from infrastructure development to environmental research. Traditional methods such as drilling, tunneling, and excavation often require substantial resources, manpower, and heavy machinery. These processes can be costly, time-consuming, and environmentally disruptive. In response to these challenges, autonomous burrowing robots have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, offering efficient and less invasive solutions.
One of the most promising advancements in this field is the horizontal self-burrowing robot, a robotic system capable of autonomously navigating and burrowing underground without the need for extensive human intervention. This cutting-edge technology is the subject of a US patent application, highlighting its potential to revolutionize subsurface operations.
With industries such as construction, agriculture, and space exploration standing to benefit, this article delves into the patent application details, the robot’s key functionalities, potential applications, and the future of autonomous underground systems.
Understanding the Horizontal Self-Burrowing Robot
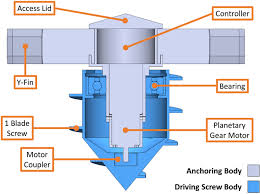
2.1 What is a Horizontal Self-Burrowing Robot?
A horizontal application self-burrowing robot is an autonomous machine designed to move underground while creating minimal surface disturbance. Unlike conventional tunneling machines that rely on large-scale excavation, this robot employs advanced burrowing mechanisms to propel itself forward through soil, sand, or other underground materials.
The primary advantage of this robotic system is its ability to navigate horizontally without the need for trenching. This feature is particularly beneficial for applications like underground utility installations, environmental monitoring, and geological surveys. By utilizing smart algorithms and real-time sensor data, these robots can adjust their path dynamically, avoiding obstacles and optimizing their burrowing efficiency.
2.2 Core Components and Mechanisms
The horizontal self-burrowing robot integrates multiple advanced components that enable efficient underground movement. The key elements include:
- Autonomous Navigation System – Equipped with AI-driven algorithms, this system allows the robot to analyze soil conditions, detect obstacles, and adjust its trajectory accordingly.
- Burrowing Mechanisms – These may include rotating drills, augers, or bio-inspired soft robotics designed to mimic natural burrowing organisms such as earthworms or mole crickets.
- Power Source and Control Systems – The robot can be powered by internal batteries, external tethers, or wireless energy transfer systems, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Sensors and Communication Modules – These components enable real-time monitoring, data transmission, and control adjustments to maintain efficient movement and direction.
2.3 How It Works
The robot’s burrowing process typically follows these steps:
- Surface Entry: The robot is deployed into the ground at a designated entry point.
- Path Planning: The onboard AI system analyzes subsurface conditions and determines the optimal route.
- Burrowing Action: Using its advanced mechanisms, the robot begins burrowing horizontally, adjusting its speed and force based on soil resistance.
- Obstacle Detection and Evasion: Sensors detect underground obstacles, enabling the robot to navigate around them without manual intervention.
- Data Collection and Transmission: The robot transmits real-time data to an external control unit, allowing operators to monitor its progress.
This autonomous functionality ensures precision and efficiency, making the technology a game-changer in subsurface exploration.
US Patent Application Overview
3.1 Background and Motivation Behind the Patent
The patent application for the horizontal self-burrowing robot stems from the increasing demand for efficient underground excavation technologies. Traditional methods, such as trenching and micro-tunneling, are often disruptive, expensive, and inefficient. As industries seek more sustainable solutions, robotic systems like this offer a less invasive and cost-effective alternative.
The innovation addresses critical pain points, including precision excavation, environmental conservation, and automation. By reducing the need for extensive digging, the technology minimizes landscape disruption and accelerates underground infrastructure deployment.
3.2 Key Claims and Innovations in the Patent
The US patent application details several unique aspects of the horizontal self-burrowing robot, including:
- Smart AI Navigation: The ability to self-adjust its trajectory based on real-time underground mapping.
- Energy-Efficient Burrowing Mechanism: Use of low-energy consumption techniques for prolonged operational cycles.
- Adaptive Material Design: Enhanced structural composition for durability in diverse soil conditions.
- Remote Operation and Monitoring: Wireless control capabilities for real-time adjustments.
These innovations position the robot as a pioneering technology in underground excavation and automation.
3.3 Patent Filing Process and Status
The patent application follows a standard process that includes filing, review, examination, and approval. While details of its approval timeline may vary, the filing underscores the growing interest in autonomous burrowing solutions. Competitors and other industry players are closely monitoring developments in this space, indicating a significant shift in subsurface technologies.
Potential Applications and Industry Impact
4.1 Civil and Infrastructure Engineering
The horizontal self-burrowing robot is a game-changer for underground utilities, including fiber optic cables, pipelines, and sewage systems. By eliminating the need for disruptive trenching, urban infrastructure projects can be executed faster and with minimal surface impact.
4.2 Environmental and Agricultural Uses
In agriculture, the robot can aid in soil aeration, root analysis, and subsurface irrigation. Environmentalists can also leverage it for underground soil sampling and contamination assessment, reducing the need for invasive excavation.
4.3 Military and Defense Applications
The defense sector sees potential in using self-burrowing robots for covert tunneling operations, underground surveillance, and landmine detection, enhancing security operations.
4.4 Space and Extraterrestrial Exploration
NASA and space agencies can deploy burrowing robots for lunar and Martian soil exploration, supporting planetary research and potential future colonization.
Challenges and Future Development
Despite its promising capabilities, challenges such as power efficiency, material durability, and regulatory approvals remain. Researchers are working on enhanced AI models, self-repairing materials, and improved sensor accuracy to overcome these limitations. The future of autonomous burrowing robotics looks bright, with potential integrations in swarm robotics and AI-driven subsurface mapping.
Conclusion
The US patent application for the horizontal self-burrowing robot marks a technological milestone in underground automation. By combining AI, adaptive burrowing mechanisms, and autonomous control, this innovation is set to redefine subsurface exploration across multiple industries. As technology advances, the potential for further enhancements and wider adoption grows, making the future of burrowing robotics an exciting frontier.
