Introduction
In the world of project management, staying within budget while ensuring timely completion is a significant challenge. Whether in construction, software development, manufacturing, or any other industry, controlling costs is crucial for project success. A project that goes over budget can lead to financial strain, delays, and even failure. This is where performance metrics such as the Cost Performance Index (CPI) come into play.
CPI is a critical measurement in Earned Value Management (EVM) that helps project managers assess cost efficiency and make informed decisions. By understanding CPI, project stakeholders can identify financial risks early, adjust strategies, and improve cost performance. This article explores the concept of CPI, its formula, significance, real-world applications, and strategies to enhance cost efficiency.
Understanding the Cost Performance Index (CPI)
Definition and Role of CPI in Project Management
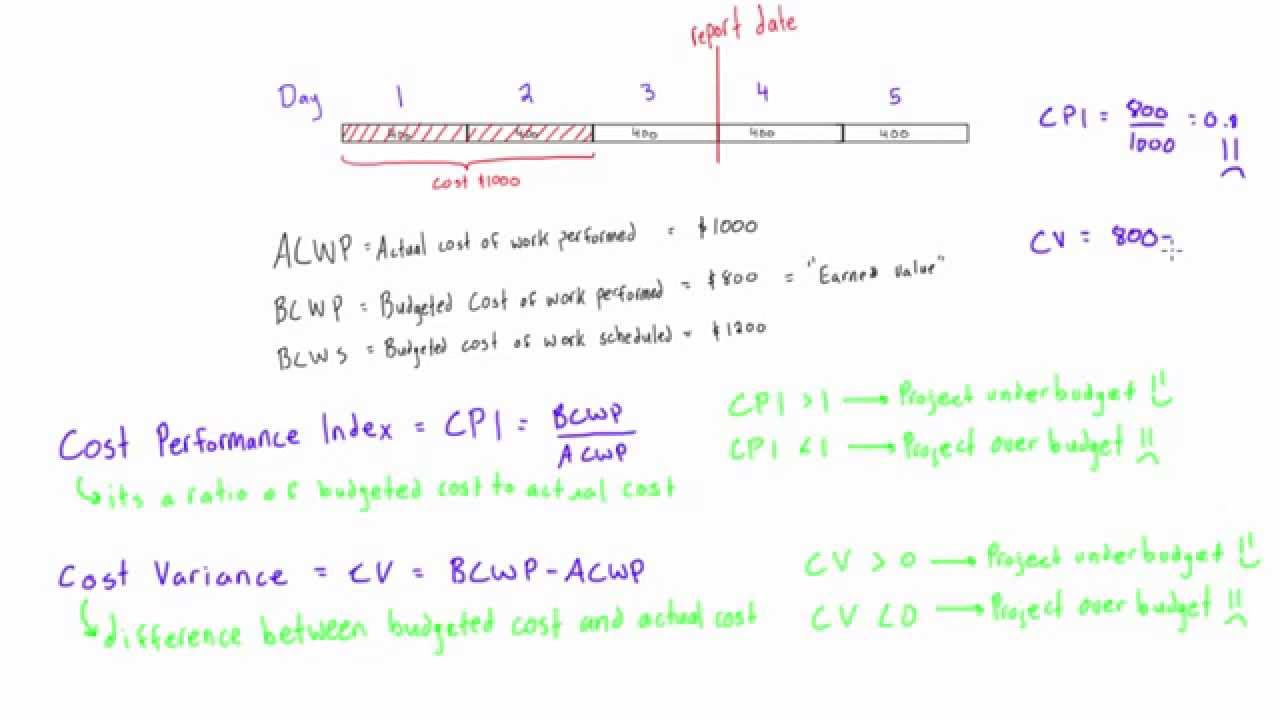
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a key project management metric that evaluates how efficiently a project is utilizing its budget. It compares the earned value (EV) of work completed to the actual cost (AC) incurred, providing a numerical representation of cost efficiency.
Formula for Calculating CPI
The standard formula for calculating CPI is:
Where:
- EV (Earned Value) represents the value of work actually performed.
- AC (Actual Cost) is the total cost incurred for the completed work.
Interpreting CPI Values
The CPI value provides critical insight into a project’s cost efficiency:
- CPI > 1: The project is under budget (efficient cost performance).
- CPI = 1: The project is exactly on budget.
- CPI < 1: The project is over budget (inefficient cost performance).
Understanding and monitoring CPI throughout a project lifecycle enables proactive cost control, ensuring financial success.
Importance of CPI in Project Management
Cost Control and Budget Forecasting
CPI plays a crucial role in budget forecasting and cost control. By continuously monitoring CPI, project managers can predict cost overruns and take corrective action early. For example, if the CPI is less than 1, adjustments such as optimizing resource allocation or renegotiating supplier contracts can be implemented to bring costs back on track.
Relationship Between CPI and Other Metrics
CPI is often used alongside the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) to give a comprehensive view of project performance. While CPI focuses on cost efficiency, SPI measures schedule efficiency. A balanced CPI and SPI indicate a well-managed project.
Decision Making and Risk Mitigation
By leveraging CPI data, project managers can make informed decisions regarding cost-saving strategies, vendor negotiations, and budget reallocations. Early identification of cost overruns allows for timely intervention, reducing financial risks.
Calculating and Analyzing CPI in Real-world Scenarios
Step-by-step Breakdown of CPI Calculation
Consider a project where:
- The planned budget for a task is $100,000.
- The work completed so far has an earned value (EV) of $80,000.
- The actual cost (AC) incurred is $90,000.
Using the formula:
Since CPI is less than 1, the project is over budget. Immediate corrective action is needed to prevent further financial strain.
Industry-specific CPI Applications
- Construction Industry: A low CPI might indicate inefficient labor use or material wastage.
- IT & Software Development: CPI can highlight unexpected development costs due to technical challenges.
- Manufacturing: CPI helps track production efficiency and material cost fluctuations.
Strategies for Improving CPI and Enhancing Cost Efficiency
Best Practices for Maintaining a Healthy CPI
To achieve a CPI of 1 or higher, project managers should adopt the following strategies:
- Regular Cost Audits: Frequent financial reviews help detect discrepancies early.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Assigning tasks to the most efficient team members boosts productivity.
- Improved Vendor Management: Negotiating better pricing and terms with suppliers can control costs.
Cost-saving Strategies Without Compromising Quality
- Using Advanced Project Management Tools: Software like Microsoft Project and Primavera P6 help monitor CPI in real time.
- Automating Repetitive Tasks: Reducing manual workload can lower labor costs and increase efficiency.
- Preventing Scope Creep: Clearly defining project requirements prevents unplanned expenses.
Stakeholder Communication for Better Cost Performance
Maintaining transparency with stakeholders about CPI trends ensures collective efforts toward budget control. Regular progress reports, financial updates, and risk assessments foster proactive problem-solving.
Conclusion
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is an essential tool for ensuring financial efficiency in project management. By monitoring CPI values and implementing cost-saving strategies, organizations can optimize budgets, improve decision-making, and enhance overall project success.
Project managers should integrate CPI tracking into their project control mechanisms to maintain cost efficiency and achieve better financial outcomes. With proactive cost management, businesses can prevent overruns and drive projects toward success.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is a good CPI value for a project?
A CPI of 1 or higher is considered ideal, as it indicates that the project is on or under budget.
2. Can CPI alone determine project success?
No, CPI should be used alongside other metrics like the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) for a comprehensive project evaluation.
3. How often should CPI be measured?
CPI should be measured regularly, at each project milestone, to ensure effective cost control.
4. What is the difference between CPI and SPI?
- CPI measures cost efficiency.
- SPI measures schedule efficiency.
5. What are common reasons for a low CPI, and how can it be improved?
A low CPI may result from inefficient resource use, inaccurate cost estimates, or unexpected expenses. It can be improved through better budgeting, optimized workflows, and proactive financial monitoring.
6. How does CPI impact project scope and timelines?
A low CPI may indicate budget overruns, which can lead to scope reductions or extended timelines.
Are there industry-specific benchmarks for CPI?
Yes, industries may have unique CPI benchmarks based on standard cost structures and financial expectations.